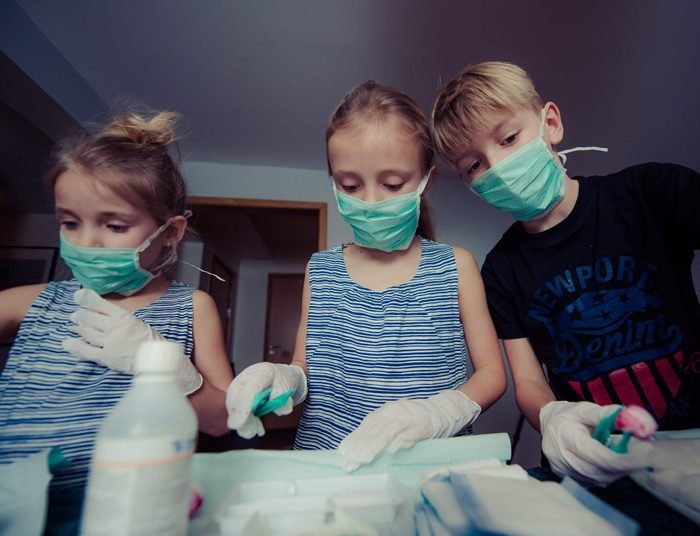
Children and young adults all over the world are slowly getting ready to get back to schools and colleges for the first time after the coronavirus struck. The World Health Organization (WHO) though has warned parents to practice extra precaution with their kids, especially in the age-group of 6 to 11.
The world body want children to wear their masks well and avoid the spread of coronavirus. Children in general face less severe virus symptoms than adults, with the elderly the most vulnerable to severe infection and death.
In a document dated August 21 on the WHO website, the world body and UNICEF said that children aged 12 and above must wear masks mandatorily when a one-metre distance cannot be guaranteed and there is probable widespread transmission in their respective areas.
It wasn’t mandatory for children between six and 11 to wear masks, which might depend on factors including the intensity of Covid-19 transmission in the area, the child’s ability to use a face mask, adequate adult supervision, said both organisations.
“Luckily, the vast majority of children who are infected with the virus appear to have mild disease or asymptomatic infection, and that’s good news,” said Maria Van Kerkhove, technical chief of the UN health agency’s emergencies programme, was quoted as saying by AP news agency.
She still cautioned that some children can develop severe cases of coronavirus and even die.
The shift comes as confirmed Covid-19 infections worldwide have surpassed 23 million and confirmed deaths have passed 809,000, according to a tally by Johns Hopkins University. Experts say the tally understates the true toll of the pandemic due to limited testing, missed mild cases and other factors.
The UN health agency for months trailed many governments in backing the widespread use of masks, a point not lost on critics, who said WHO was too slow to get on board with the benefits of general mask use.
WHO had expressed concern that people who put on masks might unwittingly spread the virus from an unclean hand to their face, and insisted that health-care providers needed masks first amid some shortages.
Since then, researchers have found that the virus can be transmitted through aerosols — tiny droplets emitted when people talk, laugh, sing or sneeze — and mask-wearing can cut down on the amount of virus that people are exposed to.
Acknowledging gaps in both research and understanding of the virus, WHO said kids under age 6 should not wear masks, while those 12 to 18 should wear them just like adults should — notably in cases where physical distancing cannot be ensured and in areas of high transmission.
WHO advises a “risk-based approach” for kids aged 6 to 11 that balances various factors. “Everyone agrees how important it is that schools are operating safely,” Van Kerkhove said. “We’ve outlined how that can be done in terms of physical distancing and hand hygiene stations, respiratory etiquette, the potential use of masks by either the workers or the children themselves.”
WHO said the current evidence suggests virus cases reported from kids stemmed mostly from transmission within households and that ‘documented transmission among children and staff within educational settings is limited’.
Parents, health officials and educators in countries around the world have been wrestling with the safety questions posed by having millions of children go back to school during a pandemic.
The WHO had first advised people to wear masks in public on June 5 to help curb the spread of the disease, but hadn’t issued specific guidance for children. On their Instagram account, they shared a video using the campaign hashtag – #WearAMask – to educate people on why masks are important and also called mask-wearers the real superheroes.